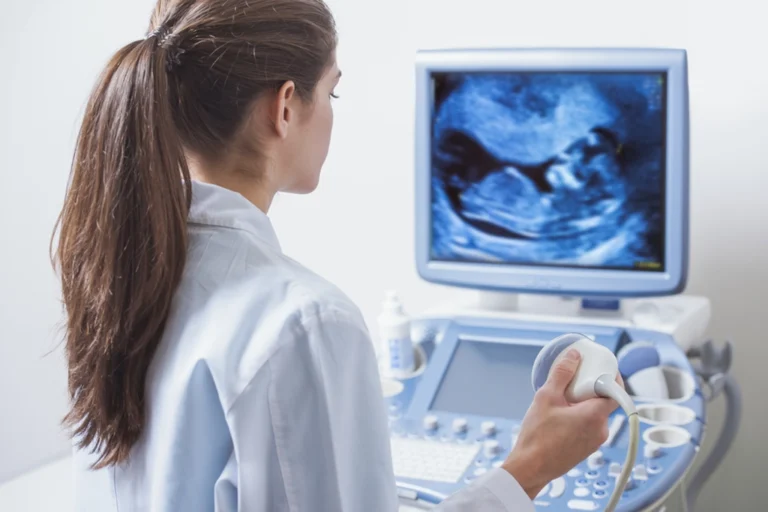
If your doctor has recommended an ultrasound, you may be wondering why this particular diagnostic imaging test is necessary. Because an ultrasound can scan nearly every organ or joint and results can be interpreted in real-time, doctors use this scan to diagnose and monitor many conditions.
Perhaps the most common reason for an ultrasound is to look at the uterus and ovaries during pregnancy to monitor the health of the organs and the baby. However, an ultrasound can be used to detect many other potential ailments and to diagnose or monitor any of the following:
- Gallbladder disease (and gallstones)
- Irregular blood flow
- Breast lumps
- Thyroid glands
- Genital and prostate problems
- Joint inflammation
- Metabolic bone disease
- Abnormal growths (tumors or cancer)
- Blood clots
- Enlarged spleen
- Aortic aneurysm
- Kidney or bladder stones
How Does An Ultrasound Work?
An ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures. These sound waves are emitted by a handheld device called a transducer, which is placed on the skin and captures the echoes produced by the sound waves bouncing off internal organs and tissues. Unlike other medical scans, an ultrasound does not require entering a machine. During your scan, you will lay on a medical bed and an ultrasound technician will use the transducer over the part of the body being scanned. The transducer will record the sound waves and they will appear as a real-time image (called a sonogram) on a screen.
Assessing Pregnancy & Fetal Development
One of the most common reasons for an ultrasound is to assess the progress of pregnancy and monitor the health of the fetus. Ultrasounds can provide valuable information about fetal development, including confirming pregnancy, estimating gestational age, detecting multiple pregnancies, evaluating fetal growth, and identifying any potential abnormalities. In certain cases, a transvaginal ultrasound may be recommended during early pregnancy or in specific gynecological situations. This type of ultrasound involves a specially designed transducer inserted into the vagina to obtain clearer images of the pelvic organs or embryos in early pregnancy. Ultrasounds play an important role in evaluating gynecological conditions such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, or abnormal uterine bleeding. They can assist in diagnosing and monitoring these conditions, providing valuable information for treatment planning.
Evaluating The Gastrointestinal & Musculoskeletal Systems
Ultrasounds are commonly used to examine abdominal organs such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. They can help diagnose conditions such as gallstones, liver disease, abdominal masses, or kidney stones. Ultrasounds are effective in assessing soft tissue injuries, such as tendon tears, muscle strains, or ligament damage. They can help determine the extent of the injury and guide appropriate treatment.
How Do I Prepare For An Ultrasound?
Most ultrasounds don’t require any preparation. For gallbladder ultrasounds, you may be required to not eat or drink ahead of your appointment. A pelvic ultrasound may require a full bladder. Please wear loose, comfortable clothing to your ultrasound, as you may be asked to remove it depending on the body part being scanned. Don’t wear any jewelry or heavily scented lotions to your appointment. Ask your doctor ahead of your scan what you need to do to prepare and follow their instructions.
At South Jersey Radiology, you can trust that no matter what the reason for your ultrasound scan, we will give you the best care possible. SJRA offers diagnostic imaging services including ultrasounds at costs up to 60% less than hospital-based imaging centers. If you are ready to schedule your ultrasound appointment, reach out to any of the following locations:
- Cherry Hill Office – Cherry Hill, NJ
- Haddonfield Office – Haddonfield, NJ
- Marlton (Greentree) Office – Marlton, NJ
- Medford Office – Medford, NJ
- Moorestown Office – Moorestown, NJ
- Mount Laurel Office – Mount Laurel, NJ
- Turnersville Office – Turnersville, NJ
- Route 73 (Voorhees) Office – Voorhees Township, NJ
- Voorhees (Carnie Blvd) Office – Voorhees Township, NJ
- Sewell (Washington Twp) Office – Sewell, NJ
- West Deptford Office – West Deptford, NJ
- Willingboro Office – Willingboro, NJ
- Women’s Center at Cross Keys – Sewell, NJ
- Women’s Center at Medford – Medford, NJ
- Women’s Center at Mount Laurel – Mount Laurel, NJ
- Women’s Center at Voorhees – Voorhees Township, NJ
Learn more about the board-certified, sub-specialized radiologists who read and interpret studies at SJRA here.
Frequently Asked Questions
An ultrasound is a versatile diagnostic imaging test used to examine various organs, joints, and tissues. It can help diagnose and monitor conditions such as gallbladder disease, irregular blood flow, breast lumps, thyroid gland issues, genital and prostate problems, joint inflammation, metabolic bone disease, abnormal growths (tumors or cancer), blood clots, enlarged spleen, aortic aneurysm, and kidney or bladder stones.
An ultrasound, also known as sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves emitted by a handheld device called a transducer. The transducer is placed on the skin over the area being examined. It captures the echoes produced by the sound waves bouncing off internal organs and tissues. The recorded sound waves create real-time images, called sonograms, displayed on a screen.
Ultrasound is commonly used during pregnancy to monitor the health and development of the fetus. It can confirm pregnancy, estimate gestational age, detect multiple pregnancies, evaluate fetal growth, and identify potential abnormalities. In some cases, a transvaginal ultrasound may be recommended to obtain clearer images of pelvic organs or early embryos.
Ultrasound is effective in examining abdominal organs such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. It helps diagnose conditions like gallstones, liver disease, abdominal masses, and kidney stones. Ultrasound can also assess soft tissue injuries, including tendon tears, muscle strains, and ligament damage, providing valuable information for treatment planning.
Most ultrasounds do not require specific preparation. However, for gallbladder ultrasounds, fasting may be necessary. A pelvic ultrasound may require a full bladder. It is advisable to wear loose, comfortable clothing as you may need to remove certain garments depending on the area being scanned. Avoid wearing jewelry or heavily scented lotions. Follow your doctor’s instructions for any specific preparation required for your ultrasound.
South Jersey Radiology offers ultrasound services at various locations including:
• Cherry Hill Office – Cherry Hill, NJ
• Haddonfield Office – Haddonfield, NJ
• Marlton (Greentree) Office – Marlton, NJ
• Medford Office – Medford, NJ
• Moorestown Office – Moorestown, NJ
• Mount Laurel Office – Mount Laurel, NJ
• Turnersville Office – Turnersville, NJ
• Route 73 (Voorhees) 73 Office – Voorhees Township, NJ
• Voorhees (Carnie Blvd) Office – Voorhees Township, NJ
• Sewell (Washington Twp) Office – Sewell, NJ
• West Deptford Office – West Deptford, NJ
• Willingboro Office – Willingboro, NJ
• Women’s Center at Cross Keys – Sewell, NJ
• Women’s Center at Medford – Medford, NJ
• Women’s Center at Mount Laurel – Medford, NJ
• Women’s Center at Voorhees – Voorhees Township, NJ